Building CMOS Inverter
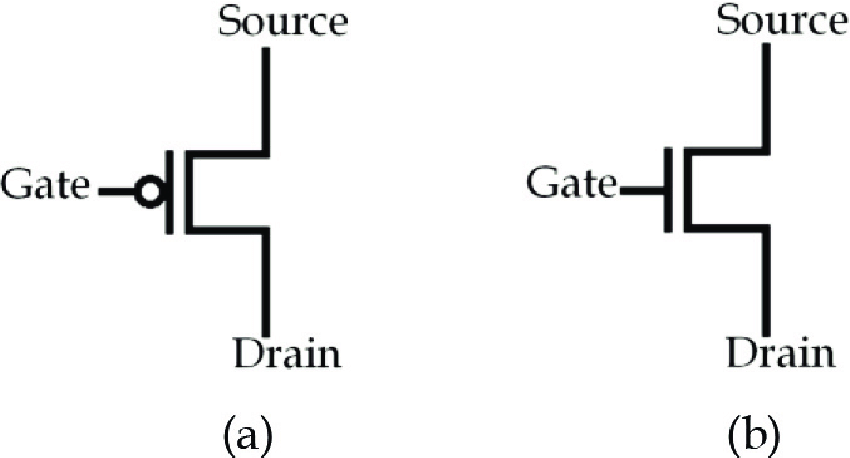
NMOS (N-type Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
An NMOS transistor conducts when the input (gate) is high. It allows current to flow between the drain and source terminals when the gate voltage is sufficiently positive. When the input is high, the drain and source are short-circuited, allowing current to flow through the transistor.
- Drain and Source Connection: When the input is high, the drain and source are connected, forming a conductive path.
- Switching Behavior: An NMOS transistor acts as a switch that allows current to flow when turned on (input high) and stops the current when turned off (input low).
PMOS (P-type Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
A PMOS transistor, on the other hand, conducts when the input (gate) is low. It allows current to flow between the drain and source terminals when the gate voltage is sufficiently negative (relative to the source). When the input is low, the drain and source are short-circuited, allowing current to flow through the transistor.
- Drain and Source Connection: When the input is low, the drain and source are connected, forming a conductive path.
- Switching Behavior: A PMOS transistor acts as a switch that allows current to flow when turned on (input low) and stops the current when turned off (input high).
Key Differences Between NMOS and PMOS:
- Conduction:
- NMOS: Conducts when the input is high.
- PMOS: Conducts when the input is low.
- Current Flow:
- NMOS: Allows electron flow (negative charge carriers).
- PMOS: Allows hole flow (positive charge carriers).
- Logic:
- NMOS: Inverted logic (on when input is high).
- PMOS: Also provides inverted logic (on when input is low).
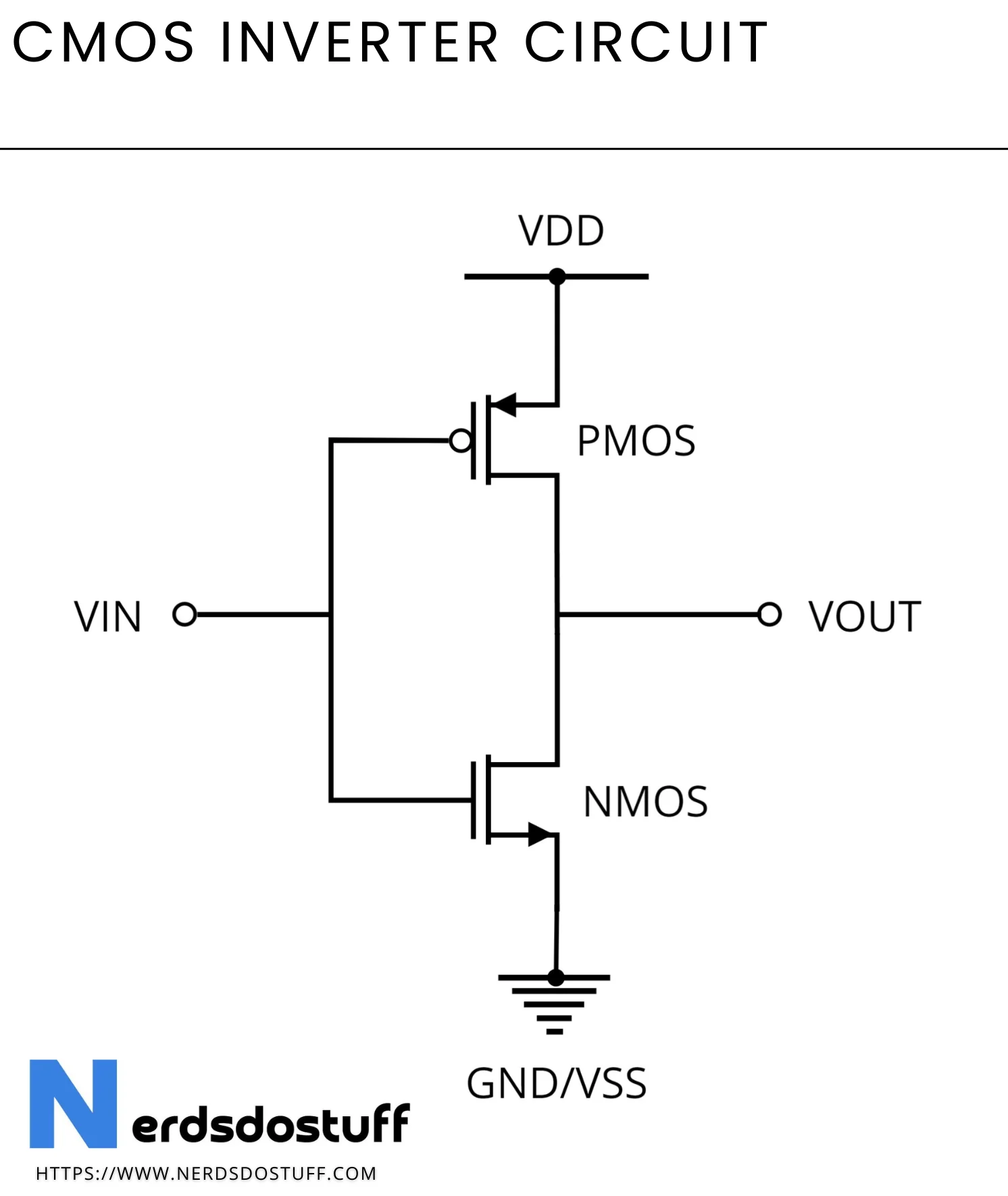
These two types of transistors are often used together in CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technology to form logic gates and other digital circuits.
CMOS Inverter from NMOS and PMOS
When Input is Zero the output is One And Vice Versa
Constructing 6T Ram Cell from CMOS Inverter
- When the write line is excited the Access Left and Access Right conducts data
- Then the and are than connected

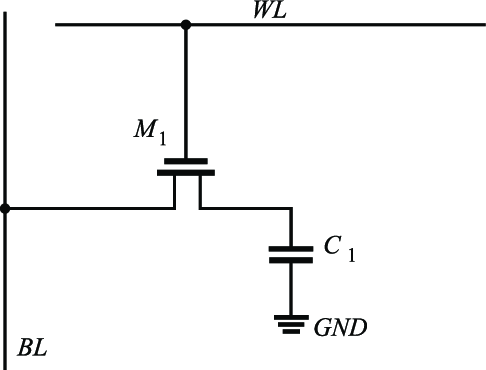
DRAM
To write data to the capacitor we must connect the capacitor with the bit line. To do that we can use an NMOS activated by write line. Then the bit is stored to the capacitor
To read data we deactivate bit line with no voltage and activate write line to check the voltage and we have gotten the data.
Capacitor
References
https://www.iue.tuwien.ac.at/phd/entner/node33.html https://www.iue.tuwien.ac.at/phd/entner/node34.html
Information
- date: 2025.02.13
- time: 11:16